Zero Trust: What is it and MDM Role

With the much needed renewed emphasis on security, and in combination with the always present topic of modern device management, I have been having lots of conversations about how to best secure customer’s environment. This is where the concepts and architecture of Zero Trust security fits so well.
Zero Trust security is not a new term or concept. It has been around for a while and it refer to security concepts and threat model that no longer assumes that actors, systems or services operating from within the security perimeter should be automatically trusted, and instead must verify anything and everything trying to connect to its systems before granting access. The term was coined by a security analyst at Forrester Research.
Today work is done from anywhere, on any device and at any time. The end-users has prompted businesses to look at their traditional cybersecurity posture and rethink it. Best practice to follow is the Zero Trust model and framework which has been adopted by many including customers and vendors.
Jorge Pereira – Dell Technologies Solutions Principal
Over the past few years, and especially in the last 12 months with the hard shift to remote work the need to understand and adopt this security model is essential for any organization hoping to mitigate cybersecurity risks.
Basic Concept:
From a device management perspective, the key core concept is that : devices should not be trusted by default, even if they are connected to a managed corporate network such as the corporate LAN and even if they were previously verified. This shifts the “burden” of trust to “what is the user trying to access” and therefore the user-based approach of modern device management.
“Zero Trust model teaches us to “never trust, always verify.”
Guiding Principle include:
The model draws on technologies such as multifactor authentication, Identity and Access Management (IAM() , orchestration, analytics, encryption, scoring, data access management and permissions and calls for governance policies based “no access unless required”
| Verify explicitly | Use least privileged access | Assume breach |
|---|---|---|
| Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points. | Limit user access with Just-In-Time and Just-Enough-Access (JIT/JEA), risk-based adaptive policies, and data protection. | Minimize blast radius and segment access. Verify end-to-end encryption and use analytics to get visibility, drive threat detection, and improve defenses. |
Implementing Zero Trust
Each piece of your computing infrastructure needs to be addressed as part of your transition strategy in order for zero-trust security to become pervasive. This also includes cultural changes to traditional thinking.
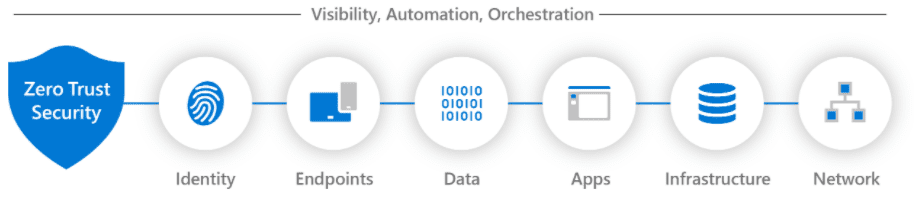
Microsoft’s Zero Trust architecture and guidelines include: Identity, Endpoints, Data, Applications, Infrastructure and Networks
Modern Device Management Connection
As we have explore on many other articles on this blog, modern device management and modern provisioning is not only here to stay, but also requires a transformational journey – Workforce Transformation. It is a paradigm shift from traditional on-prem management using images, complex local policies, and manual processes to deploy and configure devices. Modern Device Management (MDM) and its sister Modern Application Management (MAM) work together to support you endpoints bringing it together to a single pain of glass called Unified Endpoint Management.
Identity, authentication, application, data access policies based on just in time use authentication to support anywhere anytime access are the core-concepts I talk to customers everyday.
Call Out to Video Series on this topic:
An absolutely fantastic video series posted by Concept Work ( I am not associated with them but a huge fan of these guys!) on YouTube on this Microsoft’s Zero Trust Security can be found here It includes: Microsoft Zero Trust Principles or Microsoft Zero Trust Security are the guidelines that will help you secure all the six digital states of your enterprise. Learn how we have transitioned from Information system security model to cyber security model, with the proliferation of devices, applications, and services. Get insights in terms of knowing, how the old traditional security strategies are no longer enough for our current connected world.